Exploring the Brain-Oral Axis: The Interconnectedness of the Nervous and Stomatognathic Systems
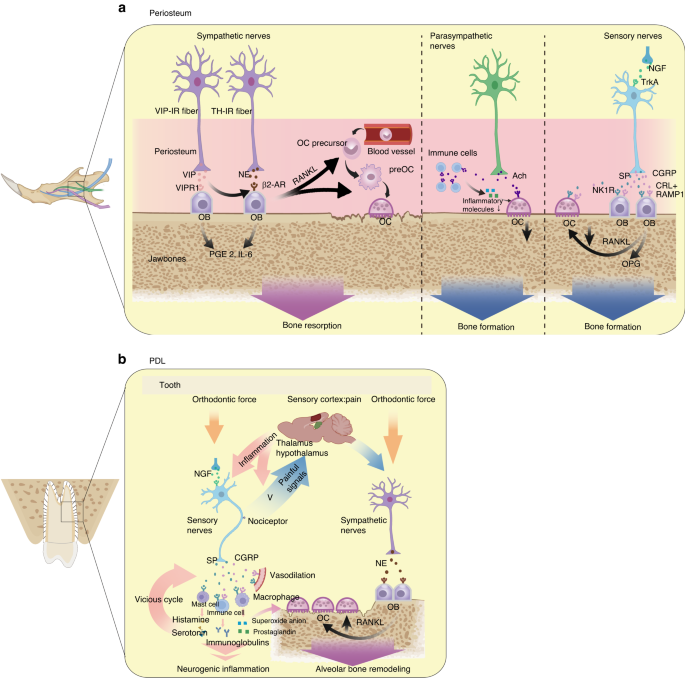
The intricate relationship between the nervous system and the stomatognathic system is increasingly recognized for its impact on overall health, leading to the concept of the "brain-oral axis." This review explores how these systems interact during development and in various diseases, highlighting the importance of neurodevelopment in craniofacial growth and the consequences of abnormalities in this cooperation. It discusses congenital disorders like trisomy 21, neurofibromatosis, and achondroplasia, emphasizing their effects on both nervous and stomatognathic systems. The review also examines how diseases such as periodontitis and neurodegenerative disorders can influence each other, suggesting that future research should focus on the regulatory mechanisms between these systems to improve prevention and treatment strategies for associated health issues.
- The nervous and stomatognathic systems are closely linked, influencing each other's development and function.
- Congenital disorders like trisomy 21 and neurofibromatosis illustrate the impact of abnormal system interplay.
- Diseases such as periodontitis can exacerbate neurological disorders and vice versa.
- Future research may enhance understanding of these interactions for better healthcare strategies.
What is the "brain-oral axis"?
The "brain-oral axis" refers to the concept that the nervous system and the stomatognathic system communicate and influence each other, affecting overall health.
How do congenital disorders affect the stomatognathic system?
Congenital disorders like trisomy 21 and neurofibromatosis can lead to physical abnormalities in the stomatognathic system, impacting oral health and function.
Why is understanding the interaction between these systems important?
Understanding the interaction is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies for diseases that affect both the nervous and stomatognathic systems.