Inflammatory Mechanisms in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Inflammatory Mechanisms in the Pathophysiology of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DN)—New Aspects 🔗
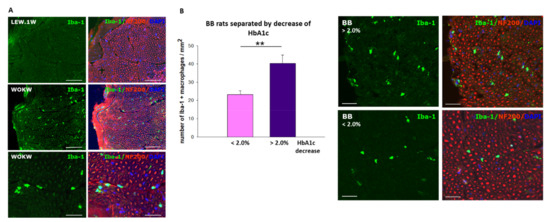
This article explores the inflammatory mechanisms contributing to diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DN). It emphasizes various factors including inflammation, iron intake, rapid blood glucose lowering, and dyslipidemia as key elements in the development of DN. The study is structured into several sections, covering the neuropathogenic roles of these factors and concluding with implications for future research and clinical practices.
- Key Factors in DN: Inflammation, iron intake, rapid blood glucose reduction, and dyslipidemia are critical.
- Focus on Inflammation: The article highlights inflammation as a primary mechanism affecting nerve health in diabetes.
- Clinical Implications: Understanding these mechanisms may guide future therapies and management strategies for DN.
What is the main focus of the article?
The article focuses on the inflammatory mechanisms that contribute to diabetic peripheral neuropathy and discusses various factors affecting its development.
How does inflammation relate to diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
Inflammation is identified as a key neuropathogenic factor, impacting nerve health and potentially leading to the progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
What are the implications for future research?
The findings suggest that further understanding of these inflammatory mechanisms could lead to better treatment and management strategies for diabetic peripheral neuropathy.